Compabloc Free Flow Heat Exchangers

 Compabloc Free Flow
Compabloc Free Flow
The Alfa Laval Compabloc Free Flow is a space-saving condenser with outstanding heat transfer efficiency, designed to meet the stringent hygiene standards of today’s active pharmaceutical ingredient (API) manufacture. The combination of hygienic design, excellent performance, low operating costs, and quick installation ensures patient safety, consistent uptime, and efficient output.
The components of the Alfa Laval Compabloc Free Flow condenser are corrosion-resistant. Its modest size allows for lower cleaning costs, making it perfect for retrofitting. The broad free-flow channel produces a minimal pressure drop, making it ideal for deep vacuum condensing jobs. Scaling is reduced, and CIP is facilitated by the turbulent flow on the cooling medium side.
Compabloc Application
Benefit
- Simple validation – entirely meets the installation standards for cGMP systems.
- All-welded construction and corrosion-resistant materials make this the ideal substitute for graphite blocks or shell-and-tube designs.
- Modern sanitary design makes cleaning quick, straightforward, and dependable; low hold-up volumes help to reduce the usage of cleaning agents.
- Perfect for retrofitting, the tiny dimensions and light weight allow you to increase capacity even in limited space.
- Certified minimal operating and maintenance expenses.
Related Industries
- Biotechnology
- Pharmaceutical Production
The Compabloc Free Flow is available in two different versions. The center component is a stack of stainless steel or alloy C22 corrugated heat transfer plates that have been welded alternately to produce channels. The condensation of the vapour on the cold plates is caused by the alternating passage of the cooling medium and the vapour. This condenser is ideal for usage in deep vacuums due to its broad free-flow channel and low pressure drop. To boost thermal efficiency and turbulence, baffles on the coolant side move the cooling fluid back and forth through the channels.
Bolts threaded through a steel frame hold the entire set of plates to pressure-retaining heads. The inlet and outlet connections are located in four detachable panels that provide simple access to all product-wetted surfaces.
Single-Pass Condenser
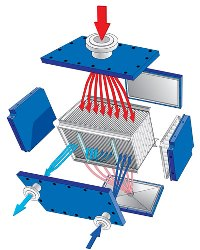
This version is appropriate when the vapour contains trace amounts of inert gas. The vapour enters through the large entrance on the top panel and condenses on the plates. The condensate drains through a sloping, drainable bottom panel.
Two-Pass Condenser
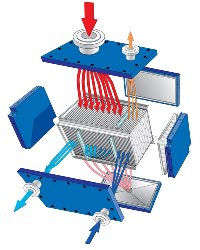
The two pass version can be used when the vapour contains a larger portion of inert gases. Main condensation takes place in the first pass where the condensable part of the vapour condenses on the plates before exiting through the sloped, drainable bottom panel.
The non-condensable vapours go through the second pass where they are sub-cooled to maximize condensation. Turbulence in the second pass helps to eliminate mist, and vacuum is easily drawn from the outlet of the second pass. With a two-pass condenser there is no need for an additional vapour separator, since separation takes place in the unit.
